Recently, the U.S. Department of the Treasury announced that it will extend the permit allowing the sale of crude oil from the Sakhalin 2 project, an oil and natural gas development project off the coast of Russia’s Far East, until June 18 next year. Major Japanese trading companies, including Mitsui & Co. and Mitsubishi Corporation, are investors in the project, making this a significant development for Japan in terms of energy procurement and economic impact.
But what exactly is Sakhalin 2? How does its revenue model work? And what impact might this news have on our daily lives, Japanese companies’ stock prices, and investors?
This article aims to clarify these questions by providing an easy-to-understand overview of Sakhalin 2, its revenue structure, and its impact on Japan. We also briefly introduce the often-confused Sakhalin 1 project.

What Are Sakhalin 1 and Sakhalin 2?
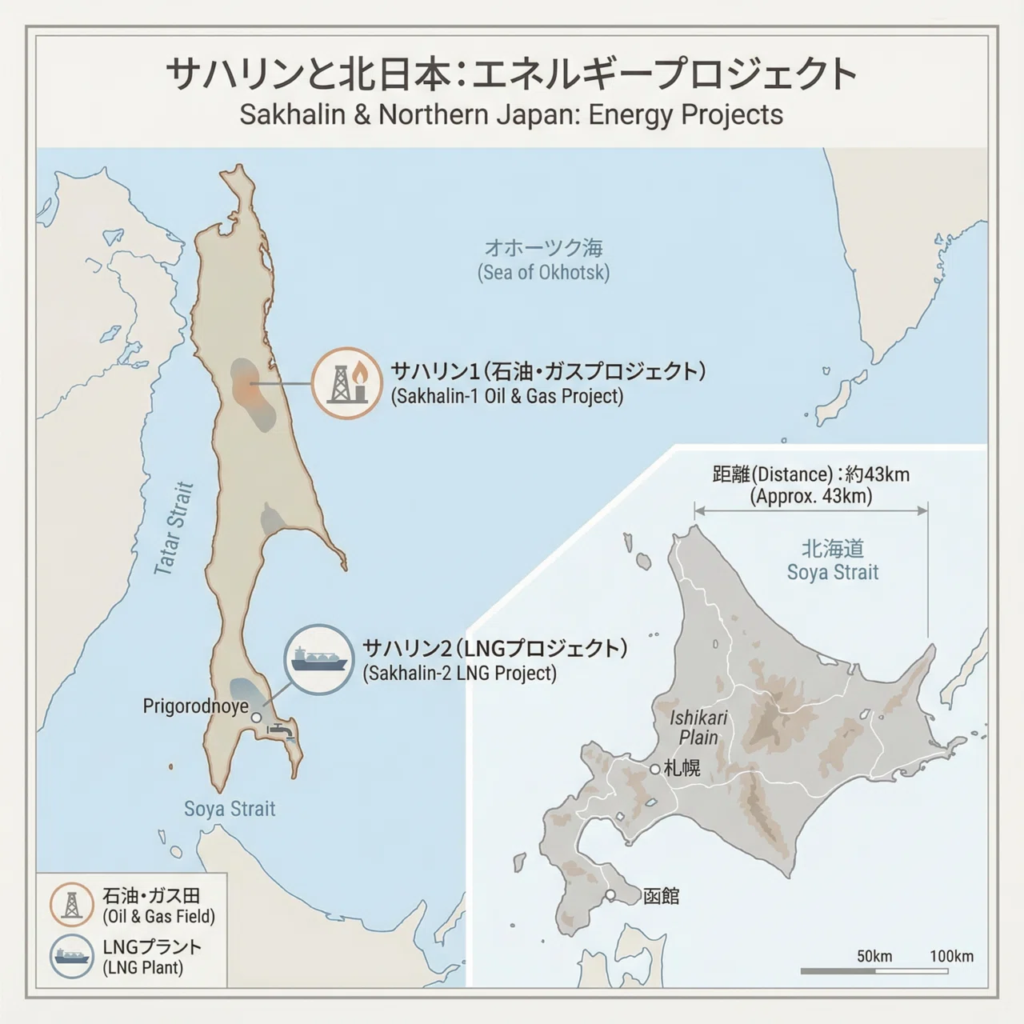
Sakhalin 1 and Sakhalin 2 are oil and natural gas development projects located around Russia’s Sakhalin Island in the Far East. These are international projects, jointly funded by energy companies from multiple countries, that extract and sell underground resources.
Since Japan relies heavily on imported energy resources, the development of Sakhalin’s resources—geographically close to Japan—is vital for ensuring a stable energy supply.
Sakhalin 1
Sakhalin 1 primarily focuses on crude oil production.
Major investors (representative examples):
- ExxonMobil (USA)
- Rosneft (Russian state-owned oil company)
- ONGC (India’s state-owned oil company)
- SODECO (Japanese consortium)
Thus, companies from the U.S., Russia, India, and Japan have jointly participated in the project.
However, since the Ukraine crisis, many Western companies have pulled back from Russian operations, making current operations unstable. Therefore, compared to Sakhalin 2, the impact of Sakhalin 1 on Japanese daily life and energy prices is relatively limited.
Sakhalin 2 (Particularly Important for Japan)
Sakhalin 2 produces both liquefied natural gas (LNG) and crude oil, making it extremely important for Japan.
Major investors and stakeholders:
- Gazprom (Russian state-owned gas company)
- Mitsui & Co. (Japan)
- Mitsubishi Corporation (Japan)
- Previously Shell (UK), now withdrawn
Currently, Gazprom leads the project, with Japanese trading companies maintaining their investments.
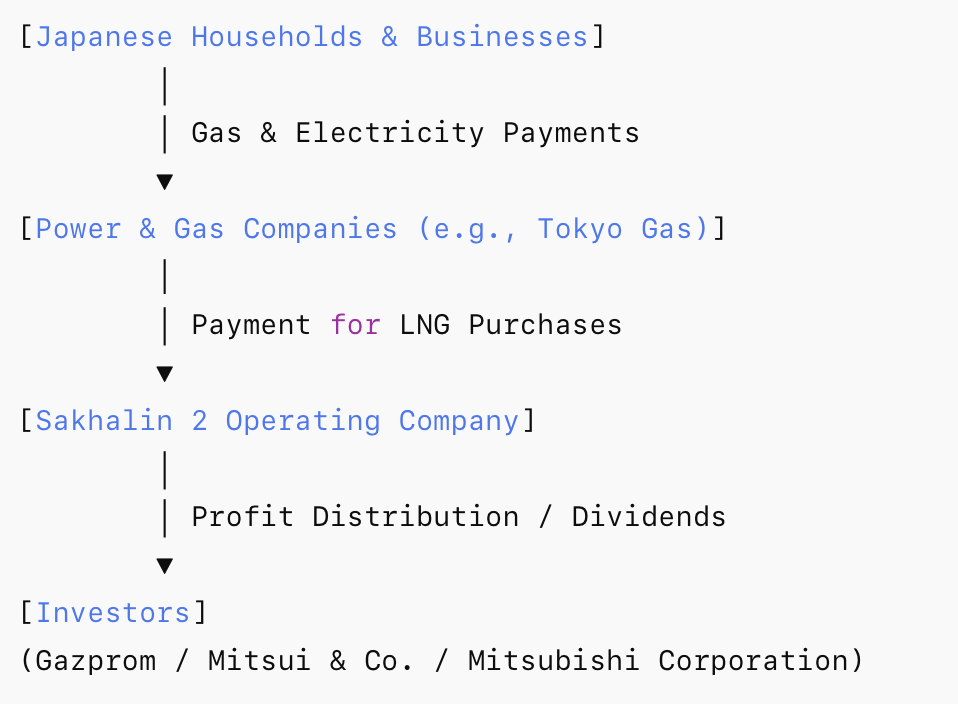
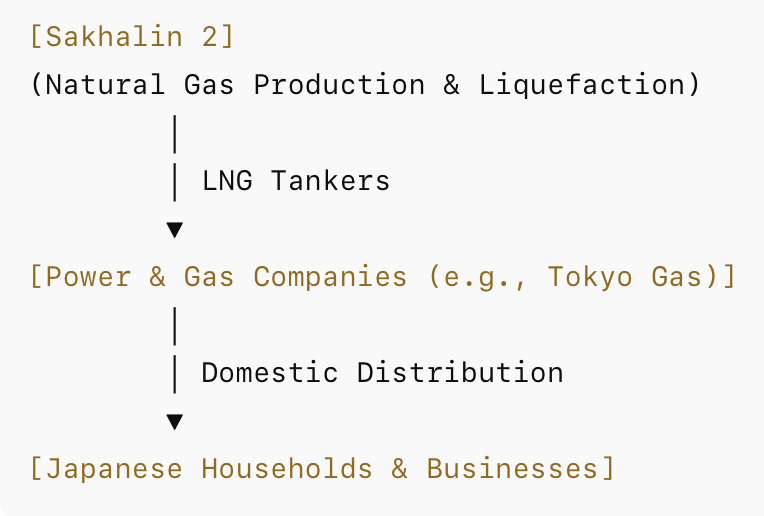
Sakhalin 2 Revenue Model
The revenue and LNG flow of Sakhalin 2 can be summarized as follows:
Revenue Flow
LNG Flow
Why Is the U.S. Treasury Involved in Japan’s Energy?
While the Treasury is not directly involved in the revenue model, it plays a key role due to sanctions against Russia.
Background:
In 2022, Russia invaded Ukraine, prompting the international community to impose economic sanctions.
Why the U.S. Treasury is involved:
Sakhalin 2 is a Russian project, but transactions are conducted in U.S. dollars and often involve international financial institutions and insurance. Therefore, U.S. sanctions apply, and the Treasury has the authority to approve or extend such transactions.
Impact on Japan:
Sakhalin 2 is a critical route for Japan’s LNG supply. Any disruption caused by the war or sanctions could lead to higher gas and electricity prices. The effects of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine are still being felt today.
Impact on Consumers and Investors
1. Consumers
- Sakhalin 2 is a key supply route for LNG to Japan.
- U.S. Treasury approval allows the continued supply of LNG.
- Reduces the risk of sudden price spikes → helps stabilize household and corporate energy costs.
💡 Key point: The permit extension provides reassurance that everyday utility costs will not surge unexpectedly.
2. Japanese Stocks
- Particularly affects the trading companies invested in Sakhalin 2, such as Mitsui & Co. and Mitsubishi Corporation.
- U.S. Treasury approval increases the likelihood that dividends and profit distributions from the Sakhalin 2 operating company remain stable.
- Stock prices may temporarily rise due to investor reassurance.
💡 Key point: From an investor’s perspective, reduced project risk is seen as a positive factor for trading company stocks.
Summary

By examining Sakhalin 1 and Sakhalin 2, we can better understand how the Russia-Ukraine war and international sanctions continue to influence Japan’s energy supply. Daily electricity and gas usage relies on overseas resource development projects and international financial transactions, highlighting the complex global network behind energy provision.
Sakhalin 2, as a major LNG supply route for Japan, also illustrates how Japanese trading companies earn revenue from international energy projects. The U.S. Treasury’s extension of the permit stabilizes supply and mitigates the risk of sudden increases in household and corporate energy costs.
Since news coverage often omits important context, we hope this explanation serves as a useful resource for deepening your understanding of trading company business, energy markets, and international economic conditions.
Note: Images included are for illustrative purposes only and may differ from actual stores or products.




コメント